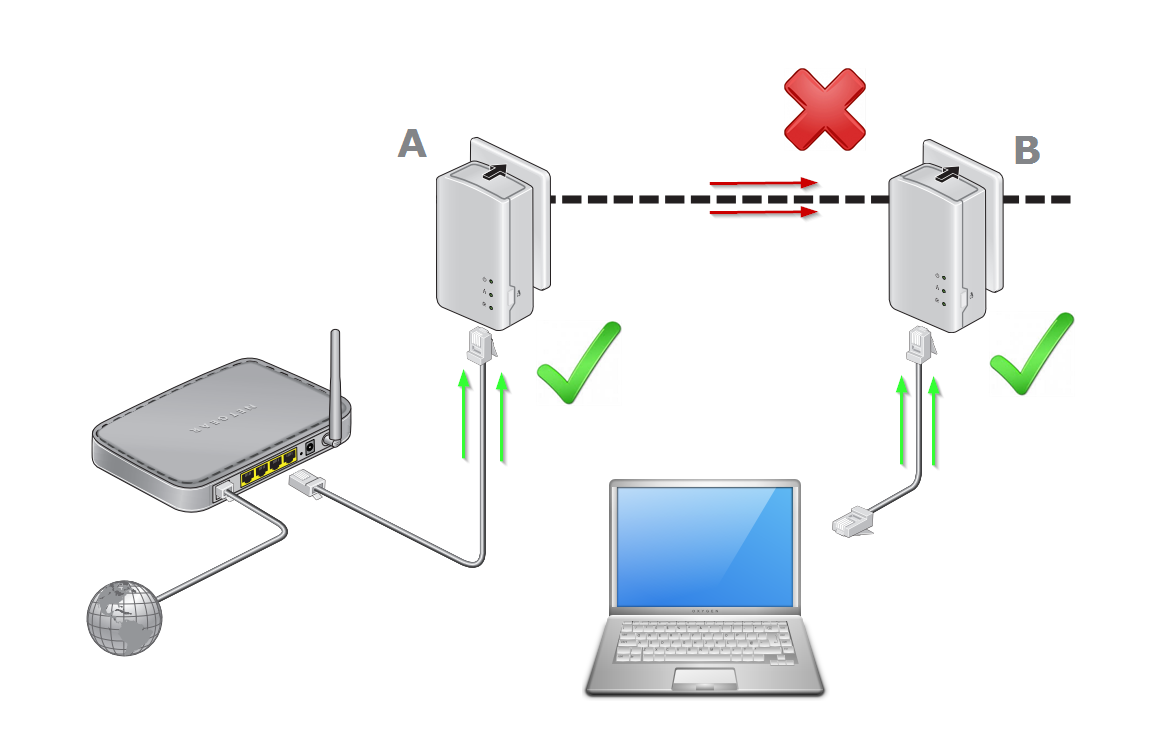
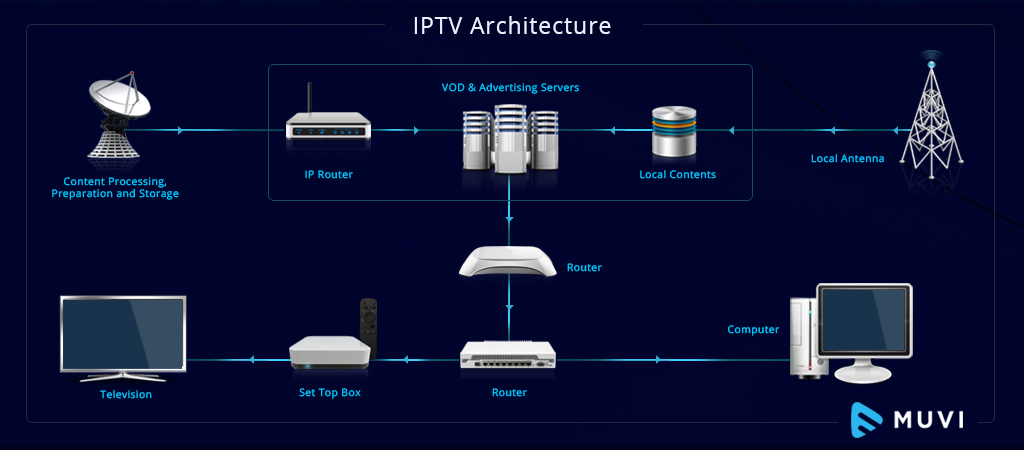
In today’s interconnected world, efficient cable routing is crucial for ensuring optimal system performance and minimizing potential issues. One critical aspect of cable management that is often overlooked is power separation. Proper power separation techniques can significantly enhance system reliability, reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI), and improve overall safety. This comprehensive guide delves into the importance of power separation in cable routing and provides practical guidelines to help you achieve a well-organized and high-performing cable infrastructure.
Understanding Power Separation
Power separation refers to the practice of physically separating power cables from data or signal cables. This separation is essential because power cables can generate electromagnetic fields that can interfere with the signals carried by data cables, leading to signal degradation, data corruption, or even complete system failure.
Improper power separation can result in various issues, including:
- Electromagnetic Interference (EMI): Power cables can induce electromagnetic fields that can interfere with the signals carried by nearby data cables, causing data errors, signal distortion, or complete signal loss.
- Crosstalk: Electromagnetic coupling between power and data cables can lead to crosstalk, where signals from one cable are inadvertently picked up by another cable, resulting in data corruption or interference.
- Safety Hazards: Inadequate separation between power and data cables can increase the risk of electrical shocks or fires, particularly in high-voltage environments.
By implementing proper power separation techniques, you can mitigate these issues and ensure optimal system performance, data integrity, and safety.
Power Separation Guidelines
To effectively implement power separation in your cable routing, follow these guidelines:
- Physical Separation: Maintain a minimum distance between power cables and data cables. The recommended separation distance varies depending on the voltage levels and cable types involved. As a general rule, a minimum separation of 6 inches (15 cm) should be maintained between low-voltage power cables and data cables, while high-voltage power cables may require greater separation distances.
- Cable Bundling: Avoid bundling power cables and data cables together. If bundling is unavoidable, use separate cable trays or conduits for power and data cables, or employ shielded cables to minimize interference.
- Grounding and Shielding: Proper grounding and shielding techniques can help reduce EMI and crosstalk. Ensure that all power cables are properly grounded, and consider using shielded data cables or installing metallic conduits or cable trays to provide additional shielding.
- Cable Routing: Plan your cable routing carefully to minimize the number of parallel runs between power and data cables. When crossing power and data cables is unavoidable, ensure that they cross at right angles to minimize electromagnetic coupling.
- Cable Management: Implement effective cable management practices, such as using cable ties, cable trays, or conduits, to maintain a neat and organized cable infrastructure. This not only improves power separation but also enhances overall system maintainability and accessibility.
Benefits of Proper Power Separation
Adhering to power separation guidelines in cable routing offers numerous benefits, including:
- Improved Signal Integrity: By minimizing electromagnetic interference and crosstalk, proper power separation ensures that data signals are transmitted accurately and reliably, reducing the risk of data corruption or loss.
- Enhanced System Performance: With reduced interference and improved signal integrity, your systems can operate at optimal performance levels, resulting in increased efficiency and productivity.
- Increased Safety: Adequate separation between power and data cables reduces the risk of electrical shocks, fires, or other safety hazards, providing a safer working environment.
- Easier Maintenance and Troubleshooting: A well-organized and separated cable infrastructure simplifies maintenance tasks and makes it easier to identify and resolve issues, minimizing system downtime.
- Compliance with Industry Standards: Many industry standards and regulations, such as those set by the National Electrical Code (NEC) or the Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA), mandate specific power separation requirements. Adhering to these guidelines ensures compliance and reduces the risk of regulatory violations.
Real-World Example: Data Center Cable Routing
To illustrate the importance of power separation, let’s consider a real-world example from a data center cable routing project I worked on. During the initial installation phase, we encountered intermittent data errors and system crashes, which were particularly problematic for mission-critical applications.
After thorough investigation, we discovered that the power cables supplying the server racks were running parallel to the data cables for extended distances. This close proximity, combined with the high-voltage power cables, created significant electromagnetic interference, causing data corruption and system instability.
To resolve the issue, we implemented a comprehensive power separation strategy. We rerouted the power cables to maintain a minimum separation distance of 12 inches (30 cm) from the data cables, ensuring they crossed at right angles when necessary. Additionally, we installed shielded data cables and grounded all power cables to further mitigate EMI.
The results were remarkable. After implementing these power separation measures, we observed a significant reduction in data errors and system crashes, leading to improved system performance and reliability. This real-world experience reinforced the importance of proper power separation in cable routing and the tangible benefits it can provide.
Conclusion
Effective power separation in cable routing is a critical aspect of ensuring optimal system performance, data integrity, and safety. By following the guidelines outlined in this guide, you can minimize electromagnetic interference, reduce crosstalk, and mitigate potential safety hazards.
Remember, power separation is not a one-size-fits-all solution. The specific requirements may vary depending on the voltage levels, cable types, and industry standards involved. It is essential to consult relevant regulations and best practices to ensure compliance and implement the appropriate power separation techniques for your specific application.
By prioritizing power separation in your cable routing strategies, you can create a well-organized and high-performing cable infrastructure that supports the seamless operation of your systems, enhances productivity, and promotes a safe working environment.