Closed-circuit television (CCTV) systems play a crucial role in modern security and surveillance. However, even the most advanced CCTV setups can experience issues, with cable-related problems being among the most common. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process of identifying, troubleshooting, and resolving various CCTV cable issues to ensure your surveillance system operates at peak performance.
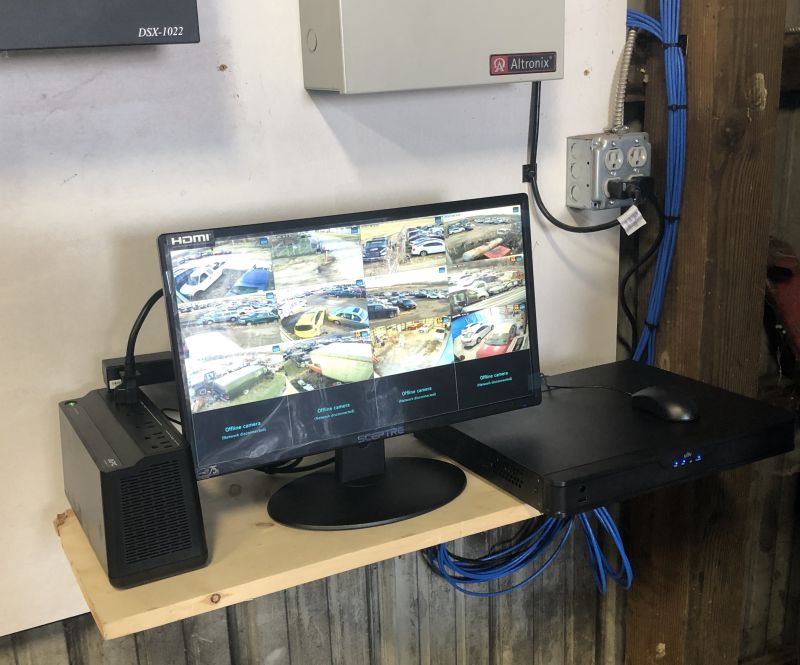

Understanding CCTV Cable Types and Their Importance
Before diving into troubleshooting, it’s essential to understand the different types of cables used in CCTV systems and their significance:
- Coaxial Cables: Commonly used in analog CCTV systems, these cables transmit video signals and sometimes power.
- Ethernet Cables: Used in IP-based CCTV systems, these cables carry both data and power (when using Power over Ethernet or PoE).
- Power Cables: Dedicated cables for supplying power to cameras and other CCTV components.
- Fiber Optic Cables: Used for long-distance signal transmission in high-end CCTV installations.
Each cable type has its own set of potential issues and troubleshooting methods, which we’ll explore in detail.
Common CCTV Cable Issues and Their Symptoms
Identifying the symptoms of cable-related problems is the first step in effective troubleshooting. Here are some common issues you may encounter:
- No Video Signal: The monitor displays a black screen or “No Signal” message.
- Poor Image Quality: Blurry, distorted, or pixelated video feed.
- Intermittent Signal: Video feed cuts in and out sporadically.
- Color Issues: Incorrect or inconsistent colors in the video feed.
- Ground Loop Interference: Horizontal bars or “hum bars” across the screen.
- Voltage Drop: Cameras turning on and off or exhibiting erratic behavior.
Now, let’s delve into the troubleshooting process for each of these issues.
Troubleshooting No Video Signal
When faced with a complete loss of video signal, follow these steps:
- Check Power Supply: Ensure all cameras and recording devices are properly powered. Use a multimeter to verify correct voltage levels.
- Inspect Cable Connections: Check that all cables are securely connected at both ends. Look for loose connectors or damaged cable jackets.
- Test with Known Good Equipment: Swap out cables, cameras, or monitors with known working ones to isolate the issue.
- Verify Camera Settings: For IP cameras, confirm network settings are correct, including IP address, subnet mask, and gateway.
- Check for Cable Damage: Inspect the entire length of the cable for cuts, kinks, or signs of rodent damage.
- Test Cable Continuity: Use a cable tester to check for breaks or short circuits in the cable.
If these steps don’t resolve the issue, the problem may lie with the camera or recording device itself.
Addressing Poor Image Quality
Blurry or distorted images often stem from cable-related issues. Here’s how to troubleshoot:
- Check Cable Length: Ensure cable runs don’t exceed maximum recommended lengths (typically 300 feet for coaxial and 328 feet for Ethernet).
- Inspect Connectors: Look for corroded, damaged, or improperly crimped connectors.
- Verify Cable Type: Confirm you’re using the correct cable type and quality for your CCTV system (e.g., RG59 for analog or Cat5e/Cat6 for IP).
- Eliminate Interference: Keep CCTV cables away from power lines and other sources of electromagnetic interference.
- Check Terminations: Ensure proper 75-ohm termination for coaxial cables to prevent signal reflections.
- Adjust Camera Settings: Fine-tune focus, iris, and other camera settings to improve image quality.
Remember, poor image quality can also result from issues with the camera lens or image sensor, so don’t rule out hardware problems.
Resolving Intermittent Signal Issues
Intermittent video signals can be frustrating to diagnose. Try these troubleshooting steps:
- Secure Loose Connections: Tighten all cable connections and consider using locking connectors.
- Check for Environmental Factors: Look for sources of vibration or movement that could be affecting cable connections.
- Inspect for Water Damage: Check for moisture ingress in outdoor installations, which can cause intermittent issues.
- Test Power Supply Stability: Use a power supply tester to ensure consistent voltage output.
- Monitor Network Traffic: For IP systems, analyze network traffic to identify potential bandwidth issues or packet loss.
- Implement Signal Boosters: For long cable runs, consider using signal amplifiers or repeaters to maintain signal strength.
Persistent intermittent issues may require professional cable testing and analysis to identify hidden faults.
Tackling Color Issues in CCTV Feeds
Incorrect or inconsistent colors in your video feed can be caused by various cable-related problems:
- Check Cable Integrity: Ensure all wires within the cable are intact and properly connected.
- Verify Correct Cable Pairing: For Ethernet cables, confirm that wire pairs are correctly matched at both ends.
- Eliminate Ground Loops: Use isolation transformers or ground loop isolators to prevent color distortion.
- Adjust Camera White Balance: Ensure the camera’s white balance settings are correctly configured for the lighting conditions.
- Inspect for EMI: Look for sources of electromagnetic interference that could be affecting color signals.
- Replace Connectors: Faulty BNC connectors in coaxial systems can cause color issues; replace if necessary.
If color problems persist after addressing cable issues, the camera’s image sensor or processing unit may be at fault.
Combating Ground Loop Interference
Ground loop interference, characterized by horizontal bars across the screen, can be particularly troublesome. Here’s how to address it:
- Identify Multiple Ground Paths: Look for instances where your CCTV system may be grounded at multiple points.
- Use Isolation Transformers: Install video isolation transformers to break ground loops in the video signal path.
- Implement Proper Grounding: Ensure all equipment is properly grounded to a single point to prevent potential differences.
- Check Power Sources: Verify that all CCTV components are powered from the same electrical circuit when possible.
- Use Shielded Cables: Employ high-quality shielded cables to minimize interference pickup.
- Consider Fiber Optics: For severe cases, switching to fiber optic cables can eliminate ground loop issues entirely.
Persistent ground loop problems may require the assistance of a licensed electrician to address underlying electrical issues.
Addressing Voltage Drop in CCTV Systems
Voltage drop can cause cameras to malfunction or shut down intermittently. Follow these steps to troubleshoot:
- Measure Voltage at Camera: Use a multimeter to check the voltage at the camera end of the cable.
- Calculate Voltage Drop: Use cable length and gauge to calculate expected voltage drop and ensure it’s within acceptable limits.
- Upgrade Power Supply: Consider using a higher voltage power supply to compensate for voltage drop over long distances.
- Implement Power Injection: For PoE systems, use midspan injectors to boost power for distant cameras.
- Increase Cable Gauge: Use a thicker gauge cable to reduce resistance and minimize voltage drop.
- Consider Local Power: For extreme distances, powering cameras locally may be more effective than long cable runs.
Always consult manufacturer specifications for acceptable voltage ranges to prevent damage to CCTV equipment.
Preventive Maintenance for CCTV Cables
Implementing a regular maintenance routine can prevent many cable-related issues:
- Conduct Visual Inspections: Regularly check cables for physical damage, especially in outdoor or harsh environments.
- Clean Connections: Keep connectors clean and free from corrosion, using contact cleaner when necessary.
- Tighten Connections: Periodically check and tighten all cable connections to prevent loosening over time.
- Monitor Signal Quality: Use built-in system diagnostics or external tools to track signal quality trends over time.
- Update Cable Documentation: Maintain accurate records of cable types, lengths, and routes for easier troubleshooting.
- Implement Surge Protection: Use surge protectors to safeguard CCTV equipment from electrical spikes and lightning.
Regular maintenance not only prevents issues but also extends the lifespan of your CCTV infrastructure.
Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques
For persistent or complex cable issues, consider these advanced troubleshooting methods:
- Time-Domain Reflectometry (TDR): Use TDR testing to locate faults in cable runs accurately.
- Network Analysis: For IP systems, employ network analyzers to identify packet loss, jitter, or other data transmission issues.
- Thermal Imaging: Use thermal cameras to identify hot spots in cables that may indicate resistance problems.
- Signal Analysis: Utilize oscilloscopes or specialized CCTV signal analyzers to diagnose complex signal issues.
- Cable Certification: Perform full cable certification testing to ensure compliance with industry standards.
- Professional Audits: Consider hiring CCTV specialists to conduct comprehensive system audits and troubleshooting.
These advanced techniques often require specialized equipment and expertise but can be invaluable for resolving stubborn issues.
When to Upgrade or Replace CCTV Cables
Sometimes, troubleshooting reveals that cable replacement or system upgrades are necessary:
- Age-related Degradation: Cables over 5-10 years old may need replacement due to natural deterioration.
- Technology Upgrades: Transitioning from analog to IP systems often requires new cabling infrastructure.
- Increased Resolution Demands: Higher resolution cameras may require upgraded cables to support increased bandwidth.
- Persistent Issues: If troubleshooting fails to resolve recurring problems, cable replacement may be the most cost-effective solution.
- Environmental Factors: Cables exposed to harsh conditions may need more frequent replacement.
- Regulatory Compliance: New security standards or regulations may necessitate cable upgrades.
When considering upgrades, factor in future expansion plans and emerging technologies to ensure long-term system viability.
Conclusion: Ensuring CCTV System Reliability
Troubleshooting CCTV cable issues requires a systematic approach, patience, and sometimes specialized knowledge. By understanding common problems, following proper troubleshooting procedures, and implementing preventive maintenance, you can significantly improve the reliability and performance of your CCTV system.
Remember that while many cable issues can be resolved through DIY methods, complex problems may require professional assistance. Always prioritize safety when working with electrical systems and consult with CCTV experts when in doubt.
By keeping your CCTV cables in top condition, you ensure that your surveillance system remains a robust and dependable component of your security infrastructure.